Determining the Effective Permissions
8 minute read
For IT security, various reports can be generated on the action area. One report shows the effective permissions for specific users to one or more directories. All users who have a permission to a specific directory will be shown in the second report. The third report, Current View, includes the permissions that are currently displayed on the IT security tab.
It is possible to create a report for Exchange which lists the permissions of selected users or groups to the mailboxes, mailbox folders, or public folders. The Exchange Overview report lists all users who have permissions to the mailboxes, mailbox folders, and public folders.
Click the button Principal Report, Directory Report or Overview Report to open the wizard to generate the reports.
To create the principal reports at least one user or group has to be selected in the User Selection before opening the wizard.
The selected node will be used as the starting point.
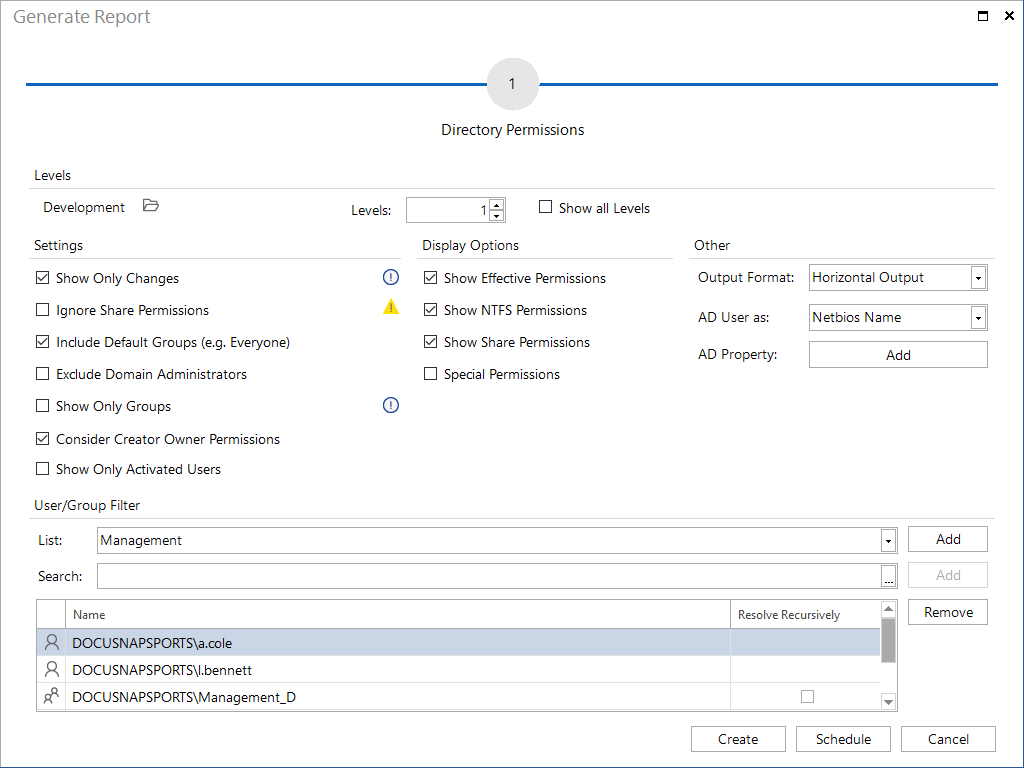
Levels
A hierarchical tree structure displays the entries for the file system, the SharePoint environment, and the Exchange servers. You can specify the number of sub-levels to be included in the report by setting the Levels field to the desired value. To include all levels, tick the Show All Levels checkbox.
Settings
If you enable the Show Only Changes checkbox, only those entries will be displayed where the effective permissions of the selected users or groups have changed. If this checkbox is not enabled, all directories, SharePoint entries, Exchange mailboxes, etc. and the corresponding user and group permissions to these items will be shown.
When calculating the effective permissions the share and NTFS permissions are used, taking into account the inheritance of permissions. By selecting the checkbox Ignore Share Permissions, only the NTFS permissions are analyzed.
For directory reports additional settings can be determined. If you check the Include Default Groups (e.g. Everyone) option, the users of default groups will also be included. Since domain administrators have full access to all directories in most cases, you can exclude them from the reports by enabling the Exclude Domain Administrators checkbox. If the Show Only Groups checkbox has been enabled, only the permissions for groups, and not those for individual users, will be included.
The Consider Creator Owner Permissions checkbox can be used to specify whether users who have been granted permissions to the folder based on the Creator Owner group should be included in the report.
If the Show Only Activated Users checkbox is selected, only active users are displayed in the report. Even if disabled users have directory privileges, they are not listed in the report.
Display Options
Usually, the report will show three blocks of permissions (effective, share and NTFS). Using the respective checkboxes you can hide or unhide information.
If the Special Permissions checkbox is enabled, the Special Permissions will be shown. Otherwise, the report will only show the Basic Permissions.
Other
For the user, directory and overview reports three different output formats are provided.
Horizontal Output:
The horizontal output lists directories, users/groups and permissions one underneath the other.Vertical Output:
The vertical output displays the directories, users/groups and permissions in a matrix.Excel Output or CSV Output:
When in the wizard the output format Excel Output or CSV Output is selected, the data is exported directly into an excel or CSV file. The file is saved in the documentation path below the respective domain.
(\Documentation Path\Company\Domain\Starting Point\Reports\PermissionsDirectory) or (\Documentation Path\Company\Domain\Starting Point\Reports\EffectivePermission)
The report displays the Netbios name of the users and groups by default. In the AD User as combobox, you can define whether the Display Name, Netbios Name, the Name, or User Principal Name is used in the report.
You can use the Add AD Property option to specify AD properties, that are then displayed for the users and groups in the report.
User/Group Filter
With the User/Group Filter users or groups can be excluded from the directory report. This can be useful, for example, so users and groups, that are not of interest, or who have access to all directories, are not listed in the reports. In the List combo box defined lists of users and groups can be added. These are compiled in User/Group Filter dialog.
Click the Add button to add the users and groups of the selected list. Via the Search text box, users and groups can be added individually. Once the first letter is entered, the matching entries are suggested. Users and groups can be added via click on the Add button. Click the  button in the Search text box to open the Advanced Search dialog. The selection of users and groups in the advanced search works the same way as when you add the user for the analysis of the effective permissions. Click the Remove button to delete a currently selected entry.
button in the Search text box to open the Advanced Search dialog. The selection of users and groups in the advanced search works the same way as when you add the user for the analysis of the effective permissions. Click the Remove button to delete a currently selected entry.
If a user is added to the filter, this user is not displayed in the directory report.
When adding a group, the application of the filter differs depending on whether the option Resolve Recursively is activated or not.
Resolve Recursively is deactivated: By adding a group to the filter without activating the Resolve Recursively option, only this specific group is included in the filter. If the filter is applied to the directory report, the group itself and all users or subgroups that obtain their permissions solely through membership in this group are not listed.
Resolve Recursively activated: When the Resolve Recursively option for a group is activated, the filter includes not only the selected group but also all direct users, subgroups, and their users. If this filter is subsequently used for the directory report, these users and groups are excluded from the directory report, regardless whether they may also have direct permissions or have inherited permissions through other groups.
The report may be exported to various file formats. Click the ![]() button and select the desired format. Clicking the desired format opens a dialog where you can select the pages to be exported. Click the + sign to expand the Settings group. Then, you can select format-specific settings. If the file should automatically be opened after the save, enable the Open After Export checkbox.
button and select the desired format. Clicking the desired format opens a dialog where you can select the pages to be exported. Click the + sign to expand the Settings group. Then, you can select format-specific settings. If the file should automatically be opened after the save, enable the Open After Export checkbox.
Scheduling
With Docusnap, you can schedule the creation of reports and have them generated automatically with the Docusnap Server at a later point in time.
Click the Schedule button to open the next step. In case you do not want to create the report using the predefined directory (documentation path), specify an alternative path. By default, the documentation path defined for the Docusnap Server will be used. If you specify an alternative documentation path, that path will be used. In addition the language can be chosen.
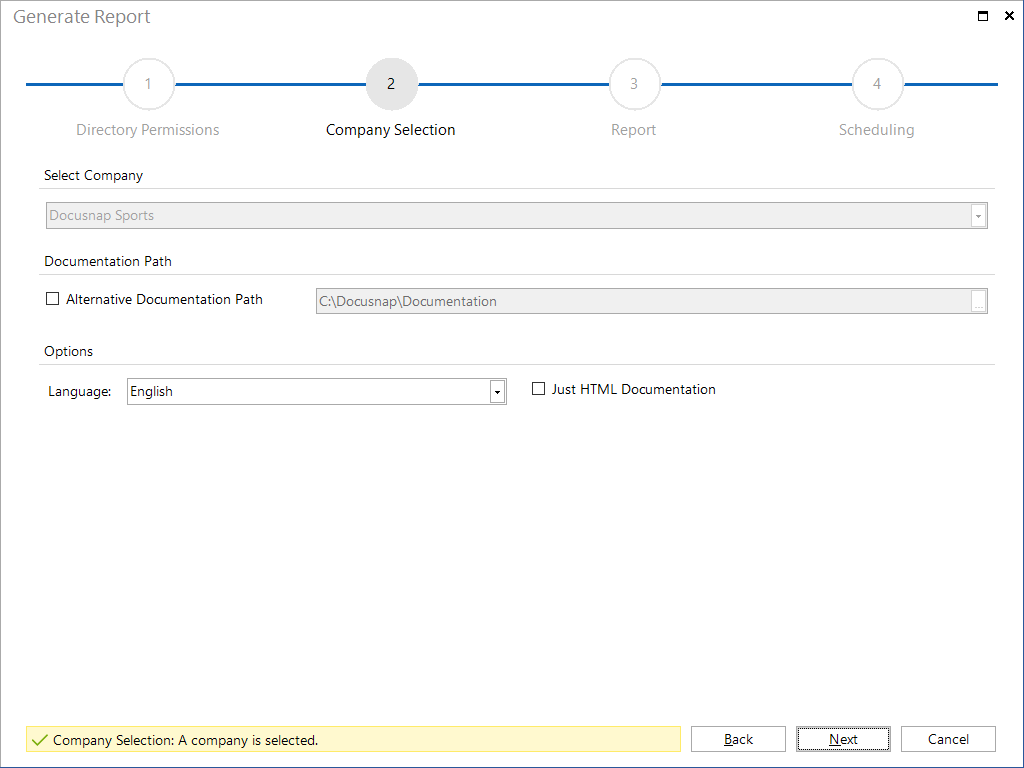
In the next step, you can select the desired report format. The following formats are available: docx, xlsx, html, odt and pdf.
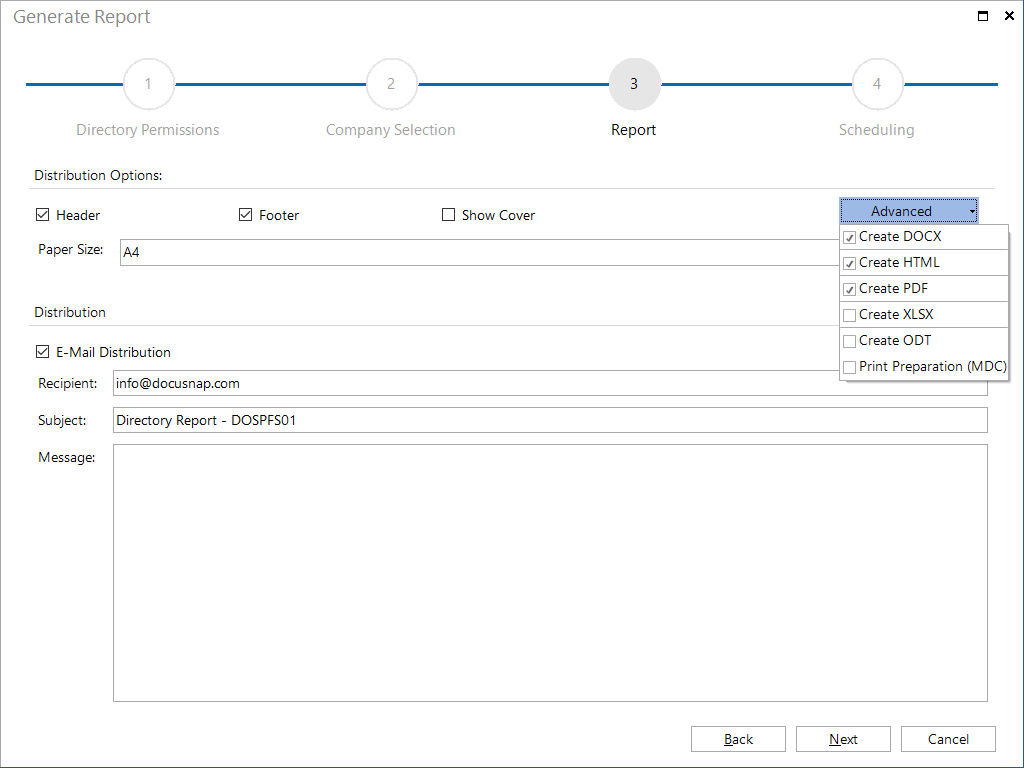
Additionally, you can specify here whether to include a cover page, a header and a footer in your report. If you do not make any changes, the settings from the Layout (CI) dialog will be used.
If you tick the E-Mail Distribution checkbox, the report will be sent to the e-mail address(es) specified below. Even if E-Mail Distribution is enabled, the reports will always be saved to the specified documentation path.
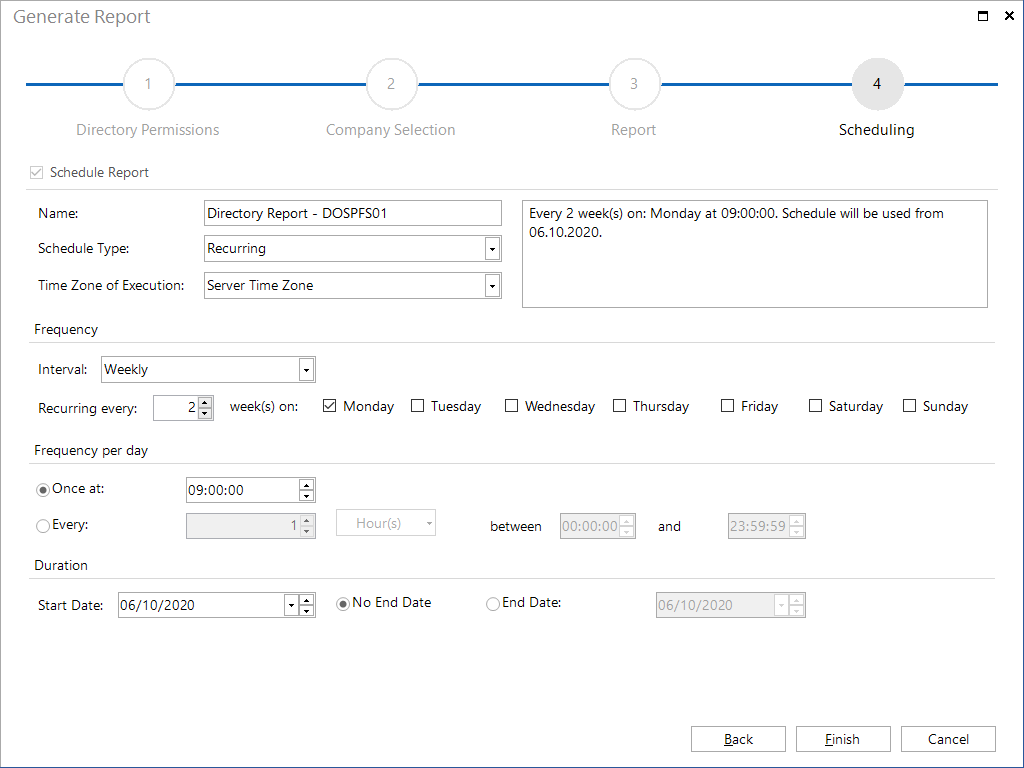
In the last step, you can define scheduling details. This step determines when and how often the report will be created. Click the Finish button to save the task.
Report Jobs
Additionally it is possible to schedule the Directory Report for several shares or DFS folder targets simultaneously and send them to a defined e-mail address. To schedule the directory reports, it is necessary to provide a CSV file that lists the desired shares or DFS folder targets. Click the Report Jobs (csv) button to open the wizard. Select the company in which the shares or DFS folder targets are located. In addition, an alternative documentation path and the language can be selected.
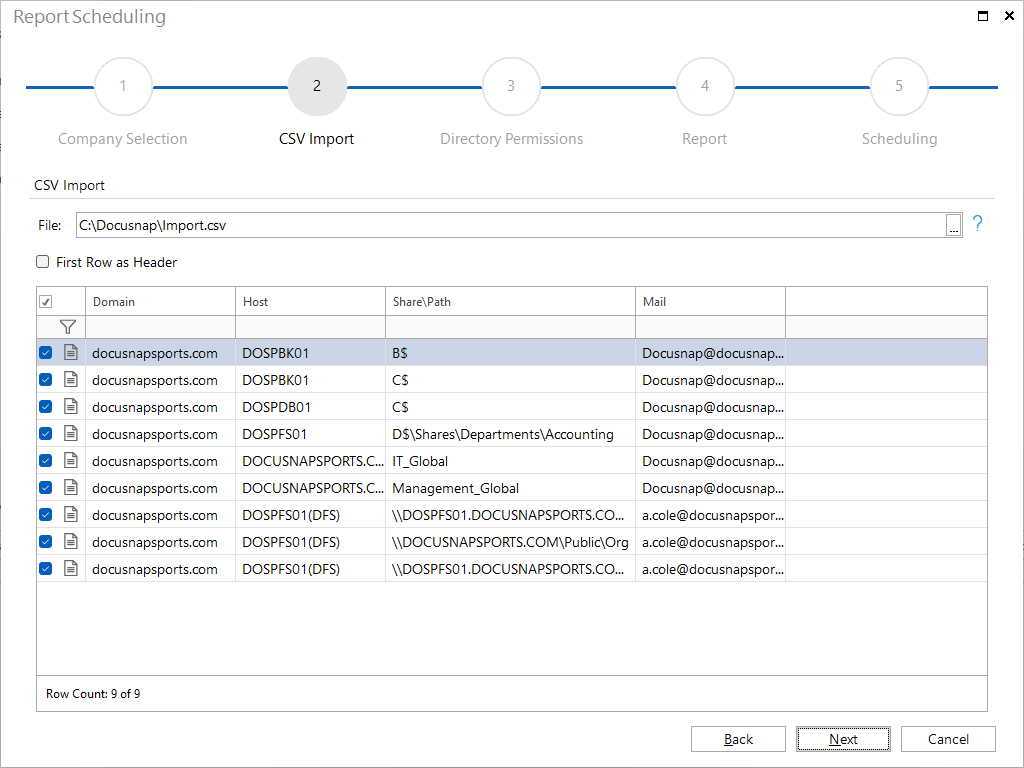
A CSV file is imported in which the desired shares and DFS folder targets are listed.
In the next step, the CSV file is imported. In the CSV file the values for Domain, Host, Share\Path and E-Mail must be listed in that order separated by “;”. If the directory report for folder targets in a DFS structure should be scheduled, (DFS) must also be written after the host so that the respective folder target can be found.
CSV example for NTFS:
docusnapsports.com;DOSPBK01;B$;Docusnap@docusnap.com
docusnapsports.com;DOSPBK01;C$;Docusnap@docusnap.com
docusnapsports.com;DOSPDB01;C$;Docusnap@docusnap.com
docusnapsports.com;DOSPFS01;D$\Shares\Departments\Accounting;Docusnap@docusnap.com
CSV example for DFS:
docusnapsports.com;DOSPFS01(DFS);\\DOSPFS01.DOCUSNAPSPORTS.COM\DFS\Archive\2010;a.cole@docusnapsports.com
docusnapsports.com;DOSPFS01(DFS);\\DOCUSNAPSPORTS.COM\Public\Org;a.cole@docusnapsports.com
For each entry is checked whether the share or DFS folder targets was inventoried for the specified host in the specified domain. The report can only be scheduled, if the directories and permissions for the specified share or DFS folder targets are available. When executing the job the report will be sent to the specified email address. If no email address is specified, the report will only be saved in the specified documentation path. Check the respective checkbox to select the shares or DFS folder targets for which a job should be created. The CSV file can be created and edited using Excel or a text editor.
Click the Next button to switch to the Directory Permissions step. In this step, the options for generating the report are selected which have already been described in this chapter. After the format of the report and the subject for the email are defined in the Reporting step, you can define in the step Scheduling when the jobs should be executed. Click the Finish button to create a job for every selected share or DFS folder target, which will be executed at the scheduled time.