SNMP Systems
8 minute read
To start the wizard for inventorying SNMP systems, click the Network Scan or SNMP button on the Inventory ribbon. The SNMP step will be displayed after you have selected a company and a domain (see: Basic Steps).
For SNMP v1, v2, and v3 systems, the system data as well as the topology information are inventoried.
Inventory of SNMP Systems
Availability Check with Ping
When performing SNMP inventory for an IP range, pings are sent by default to exclude non-existent or switched-off devices. Only devices that respond to the ping are inventoried.
Pings executed in parallel: If the firewall blocks requests due to the high number of ping queries during the inventory of IP ranges, this issue can be mitigated by limiting the number of pings executed in parallel.
Check System Availability with Ping: If the respective device does not respond to ping requests or if network settings or firewalls block ICMP requests, the inventory module cannot locate systems. By unchecking the Check System Availability with Ping option, pings are bypassed, and instead, SNMP queries are sent to all IP addresses.
- The ping check should only be disabled if it is known that devices block pings but are reachable via SNMP.
If the number of parallel pings is limited or the ping check is disabled, the inventory process may take longer.
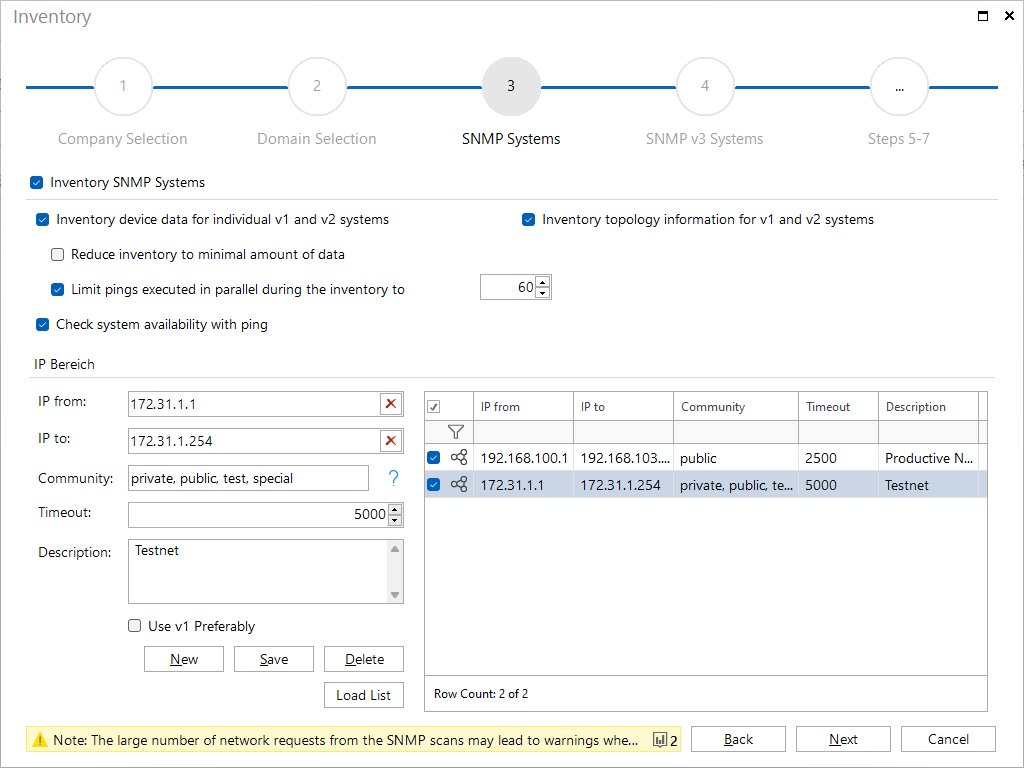
Define and manage IP ranges
Fill in the IP from, IP to, Community and Timeout fields to define the IP range to be scanned. The Description field supports the assignment of networks. The Community input field supports several values, separated by commas, which are used during the inventory.
After you have added the desired ranges to the IP Ranges list, you can specify for each range whether or not the inventory scan should be performed by enabling / disabling the checkbox next to it.
CSV import for multiple IP ranges
If several IP ranges are to be taken into account in the inventory, there is the option of importing them directly from a CSV file using the Load list button. In the CSV file, the values for IP from, IP to, Community and Timeout must be listed in exactly this order separated by “;”, the Description field is optional. If a line doesn’t match this format, this one will be omitted.
Example of a CSV file with several community values
IP from;IP to;Community;Timeout;Description
192.168.100.1;192.168.103.254;public;2500;Productive Network Outbuilding
172.31.1.1;172.31.1.254;private, public, test, special;5000;Testnet
SNMP v1/v2 fallback
In SNMP inventory, Docusnap attempts to obtain data from the SNMP device through the v2 protocol. If this request does not work, a new request is started over the v1 protocol. For some SNMP devices, a request via the v2 protocol may cause the device to be unavailable for a few seconds via SNMP. In this case, you can choose to run the v1 protocol first. If a device can not be inventoried correctly, it is possible that the required data can be successfully collected by activating the Use v1 Preferably checkbox.
Scanning Systems using the SNMP v3 Protocol
The next step is the inventory of systems that support SNMP v3.
Differences between SNMP v1/v2 and SNMP v3
The main difference between SNMP v3 and SNMP v1/v2 is that credentials can be defined for these systems instead of a community.
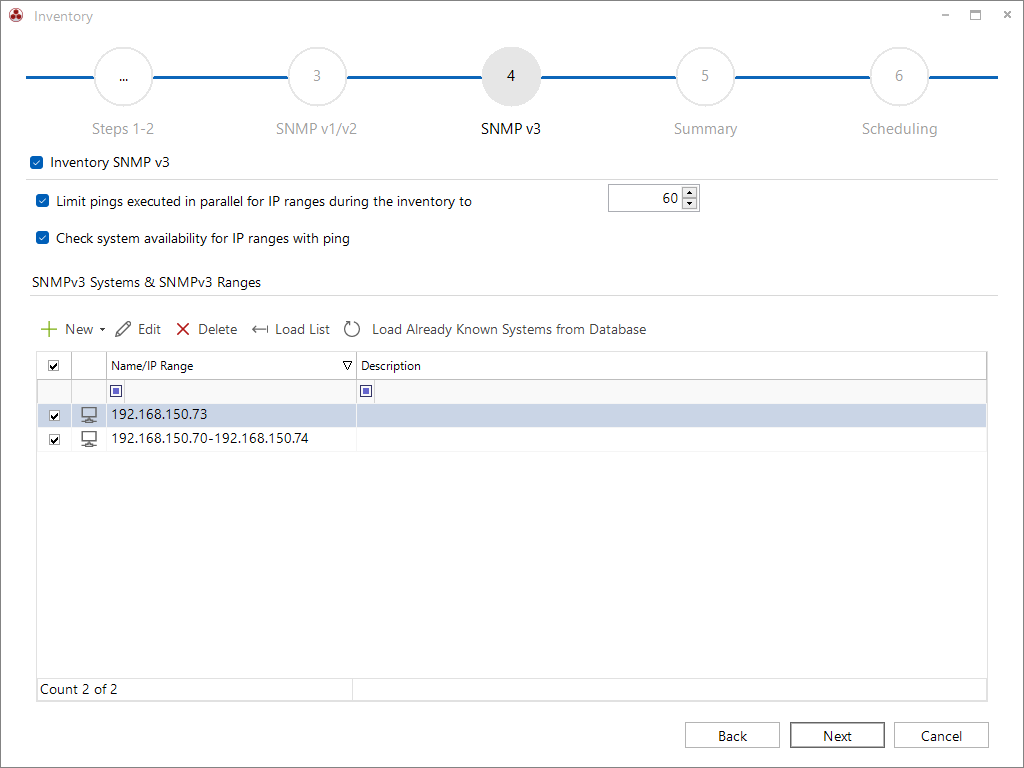
Availability Check with Ping
The two options Parallel Pings for IP Ranges and Check System Availability for IP Ranges with Ping are only relevant for the inventory of IP ranges. They are used to exclude unreachable or non-existent devices early on and optimize the efficiency of the scanning process. A detailed explanation of these options can already be found in the description of SNMP v1/v2. When a single system is manually defined, these options are not required, as the inventory process is directly applied to the specified system without first conducting a general reachability check via ping.
Inventorying individual systems with SNMP v3
The New button can be used to choose whether an inventory of Individual Systems or via an IP Range should be carried out. In the corresponding follow-up dialog, the login credentials matching the configured security level of the systems are entered. If the same credentials have already been saved for another system, they can be used for the current entry by selecting them in the Apply credentials combo box.
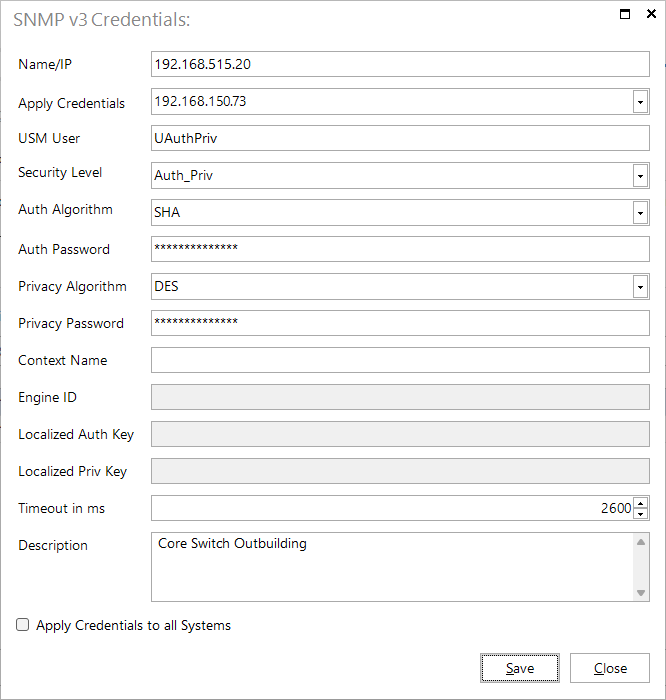
Clicking the Edit button opens the SNMP v3 Credentials dialog for the selected system and the credentials can be edited.
If several individual v3 systems with different credentials or network information are to be inventoried, there is the option of CSV import. Click on the Load list button to open the selection dialog. In the CSV file, the values must be entered in the following order, separated by “;”: System name or IP address; USM user; Auth algorithm; Auth password; Privacy algorithm; Privacy password; Context name; Timeout. If the other v3 systems have the same credentials, it is sufficient to specify only the system name or IP address. If new credentials are specified, these in turn apply to further entries.
Example for CSV file
ASWIT0001;Docusnap;SHA;secret;DES;secret;context;2600
192.168.100.3
192.168.100.4
192.168.100.5
Inventory IP ranges with SNMP v3
The inventory of IP ranges for SNMP v3 systems is similar to the inventory of individual systems. The New button can be used to open the dialog for the credentials via New IP Range. The range is then defined by IP from and IP to instead of a system name or IP address.
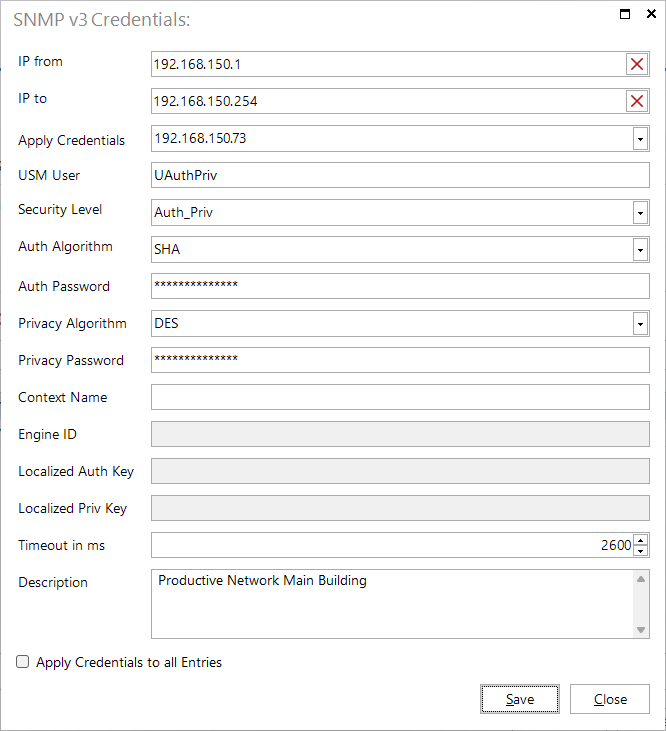
IP ranges can also be imported via CSV import using the Load List button. The structure of the CSV file remains unchanged, just enter the desired IP range instead of the system name or an IP address.
Example for CSV file IP ranges
192.168.100.1-192.168.100.150;Docusnap;SHA;secret;DES;secret;kontext;2600
192.168.100.151-192.168.100.254
Credentials are saved for each table entry in the wizard so that they are available the next time it is opened. By clicking the Load Already Known Systems from Database button SNMPv3 systems including their credentials can be reloaded. This eliminates the need to reenter devices that have already been inventoried with another wizard or that have been deleted from the wizard.
After the desired systems have been added, the checkbox can be used to specify whether an inventory of the respective system or IP range should be included.
Special aspects of the SNMP inventory
SNMP v1 and v2: Generally, Docusnap uses the SNMP v1 and v2 protocols to identify SNMP systems. Each IP address in the specified range will be checked to determine if an SNMP system is involved. If the requested IP address responds to a ping and proves itself to be a valid SNMP system, the inventory process will be performed using the SNMP protocol.
Prioritize SNMP v3: SNMP systems that require the SNMP v3 protocol, but have been listed in the IP range list for the normal SNMP scan (i.e. using the v1 and v2 protocols), will not be considered when scanning the v1 and v2 systems.
Results in the summary: If the areas overlap with simultaneous SNMP and SNMP v3 inventorying, SNMP v3 results are marked with v3 in the summary.
Identical system names: By default, Docusnap inventories SNMP systems based on their system names. If a network includes multiple SNMP systems with the same system name, the results for all corresponding systems will be grouped under this system name. If you want to obtain individual results for each of these systems, you can specify to identify SNMP systems by their DNS names (on the Inventory page of the Options - Inventory dialog).
Additional Tools Telnet/SSH
Basically, this function is similar to the Additional Tools already available in Docusnap, which optionally executes commands on the target system during the Windows inventory and then saves the execution results in Docusnap.
Additional Tools Telnet/SSH provides this feature for the SNMP inventory, but uses the Telnet or SSH protocols for data retrieval. Data retrieval via this function is currently only possible for SNMP devices of type Switch.
To use this feature in SNMP inventory, it must be enabled in the Options - Inventory dialog in the Show Features section of the wizard by selecting the Telnet/SSH (Preview) additional programs option.
This optional inventory step allows to select previously inventoried switches and to query additional information with an appropriate command sequence.
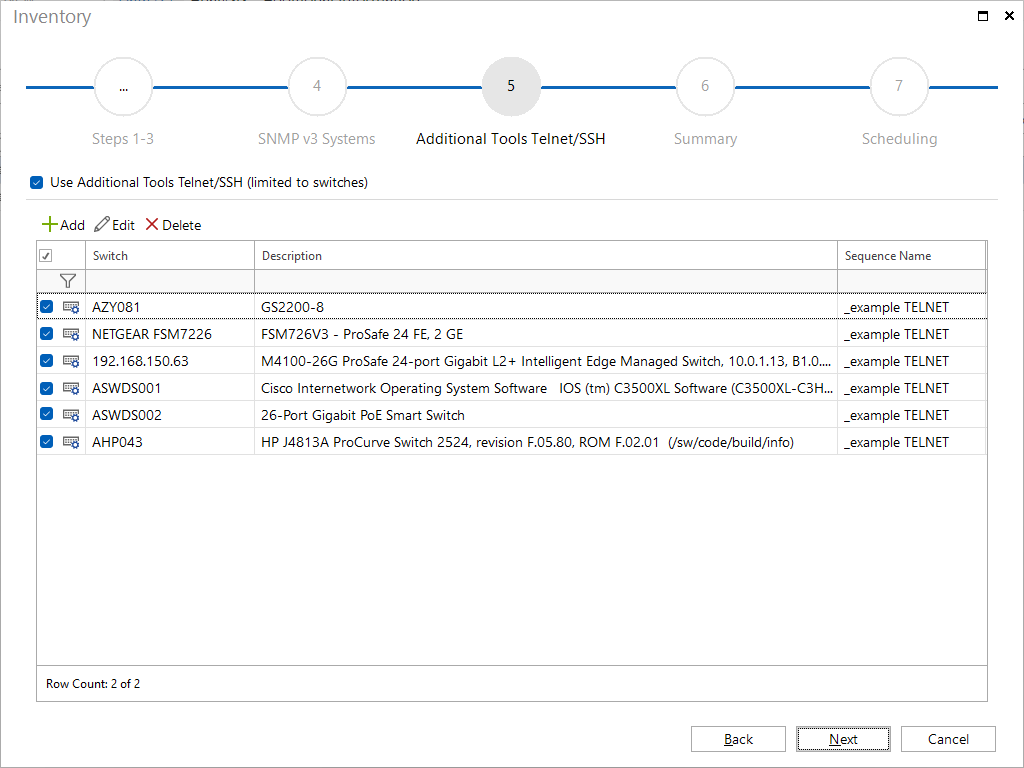
You can use the Add button in the subsequent dialog to specify the command sequences for all switches already entered.
The timeout value defines how long Docusnap waits for a response from the SNMP device before aborting the sequence. The user and password for the login must also be entered. The user entered here must have the appropriate rights. With HP switches, for example, it would be possible to log on to the switch as “Operator”. However, this user is not authorized to read out the switch configuration. The user “admin” is required for this.
Finally, the dialog can be exited via the Save button or the credentials can be verified beforehand via Check connection and save.
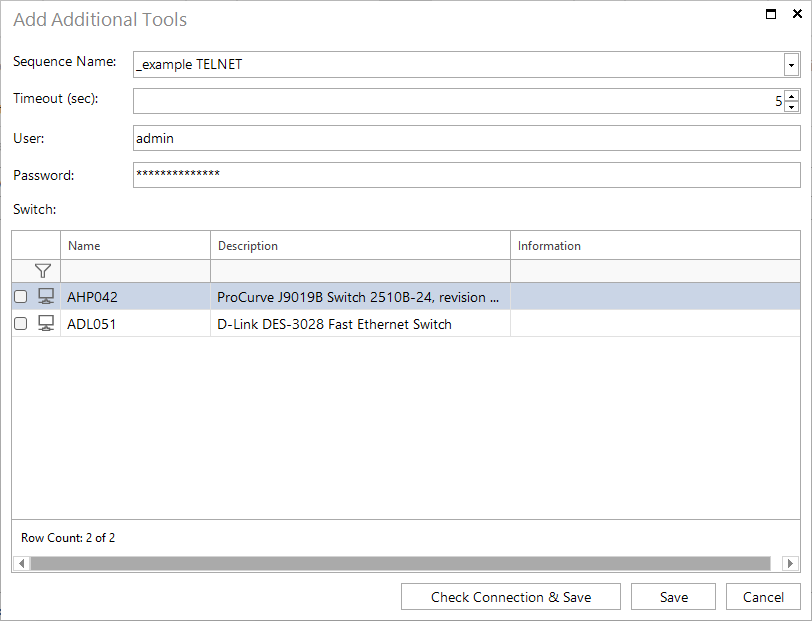
Docusnap provides two simple templates for command sequences. Here, a configuration query is created on a switch (without manufacturer reference). The example is available for calling via Telnet and via SSH.
Other command sequences can be created by the user in the Docusnap Management.